PRODUCT
Graph, Users & Permissions.
The structure behind collaboration.
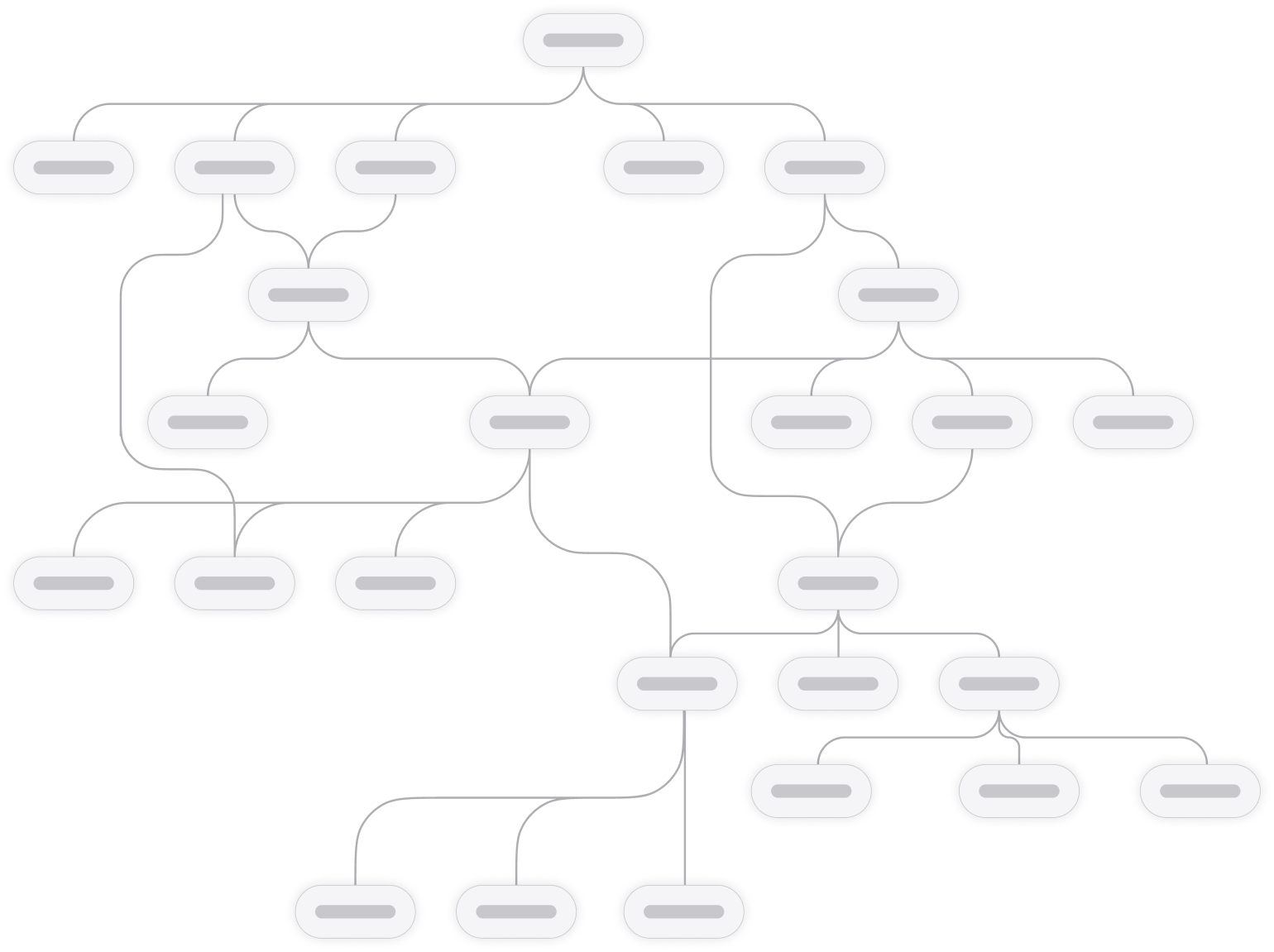
At the core of the EMS is a graph. Nodes are connected by arcs, and each node can have multiple ancestors and descendants.
On every node live the fundamental elements of the system — Layouts, Timelines, Logics, Workflows, Data items, Schemas, Sources, and Branches. This structure makes relationships explicit, flexible, and easy to reason about.
Inheritance.
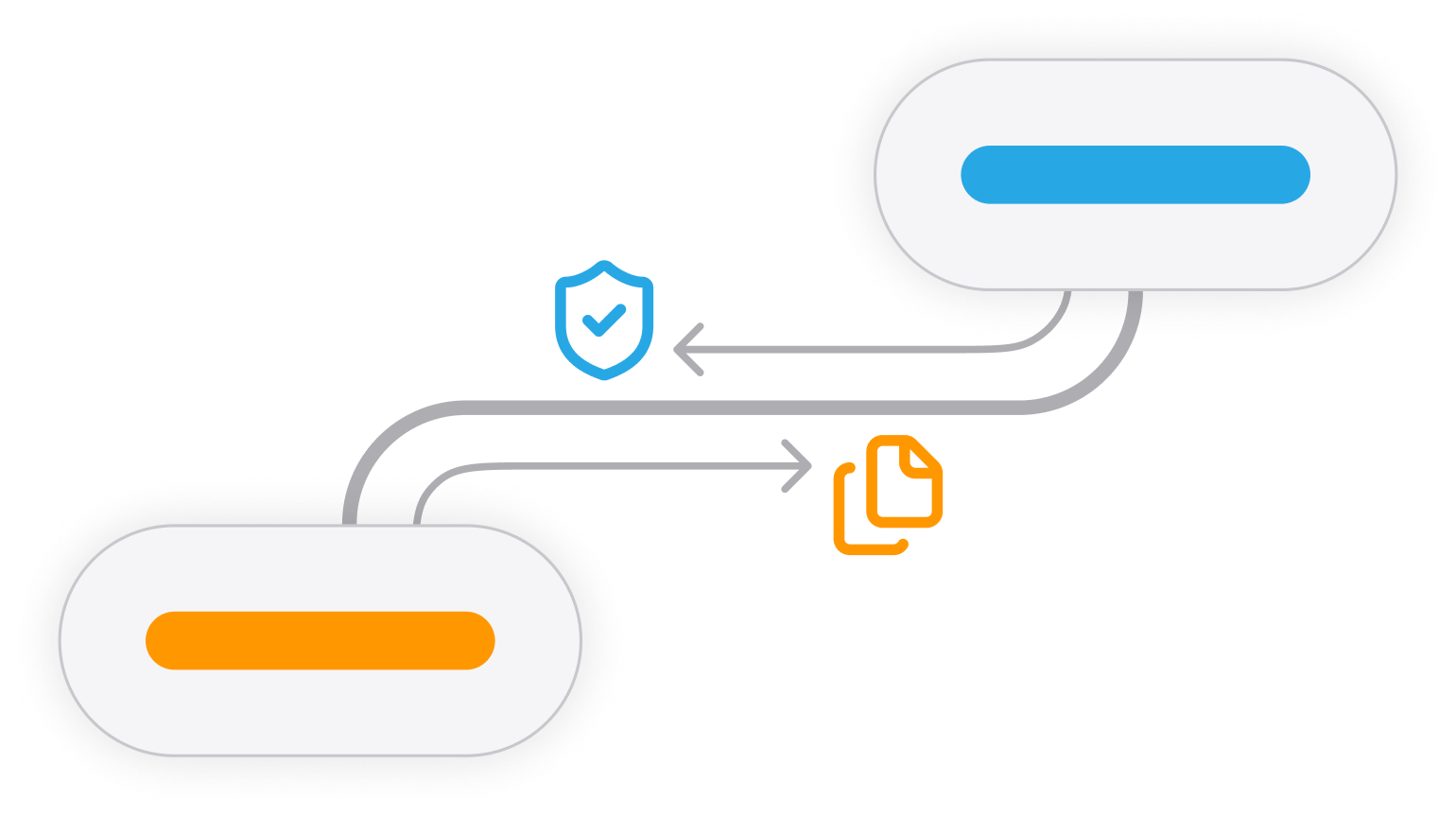
The graph provides two kinds of inheritance.
→
Work product / outputs flow upward. Layouts, Data, or Workflows defined on a node become available to its ancestors.
→
Permissions flow downward. Access granted on a node is inherited by its descendants.
This creates a balance of visibility and control: what teams produce can be reused higher up, while access can be limited as you go deeper.
EMS Users & Permission sets.
Users don’t receive permissions directly. Instead, they are assigned one or more Permission sets.
→
A Permission set defines specific rights for one or more element types (e.g. “read Layouts,” “write Timelines,” “manage Sources”).
→
Permission sets are then applied to nodes in the graph.
→
When a user has a Permission set on a node, the permissions apply to all relevant elements on that node (and inherit downward to its descendants).
This model is more flexible than static roles. Teams can be structured around exactly what they need access to, without over- or under-exposure.