PRODUCT
Workflows.
Making things happen.
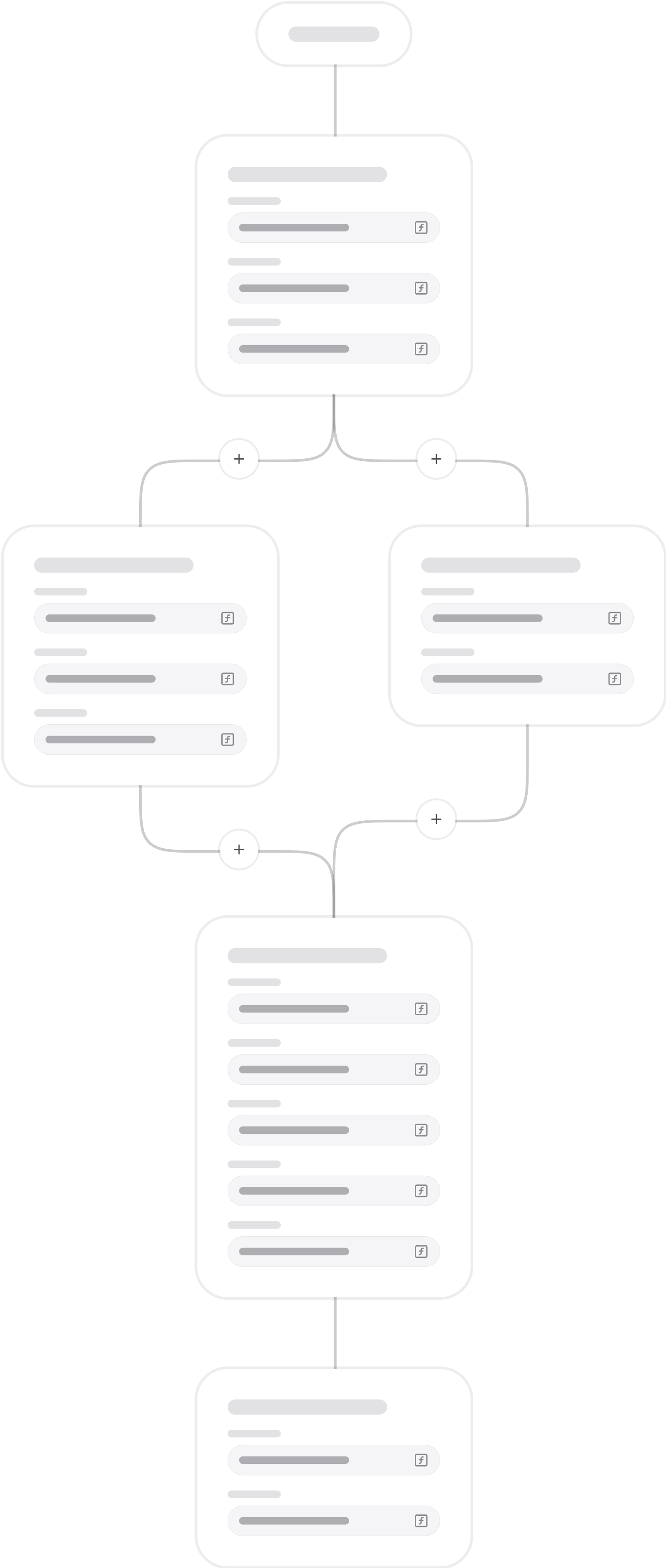
Define sequences of actions that run step by step — or in parallel when needed.
From simple UI actions like setting a variable, giving haptic feedback or starting a video, to backend operations such as signing JWT tokens, making API requests, and interacting with the Data store.
Each step can depend on one or several previous steps, giving you full control and access to their output.
Triggers.
A Workflow is always initiated by a Trigger, which can be almost anything.
→
User events (e.g click, input, focus, scroll, pointer/touch/keyboard/remote).
→
Fragment events (e.g media time update, seek, play, audio track update, appear/disappear).
→
Data/system events (e.g variable changes, persistent connections, scheduled times via Timelines).
→
External triggers (webhooks).
Try it.
Trigger this demo workflow to fetch radio stations from the Radio Browser API.
Execute count: 0
Step 1: Reset Stations variable
+500ms delay for dramatic effect.
Step 2: Fetch Radio Browser API
fi1.api.radio-browser.info/json/stations/...
Step 3: Select random station
Workflows can be scoped differently depending on use case.
→
Local: attached to a single Fragment, e.g. a play/pause workflow for a video player.
→
Shared: defined on a Layout for reuse across multiple Fragments, e.g. navigation handling.
→
Global: defined on a Graph node for universal availability, e.g. a login workflow used across all apps.
Workflow actions
Workflows are made up of actions. These are the steps you can combine to update data, call APIs, control the UI, or handle security.
Create, query, and store values inside the EMS.
Delete Source Items
List Storage Keys
Upsert Data Item
Read Source
Read Storage
Remove Storage
Set Variable
Set Context
Set Storage
Passthrough
Connect to external systems or chain workflows together.
Communicate (Real-time IO)
Execute Workflow
Send HTTP Request
Send Push Notification
Generate, sign, and verify tokens or hashes.
Sign JWT
Verify JWT
Encrypt JWT
Decrypt JWT
Generate Hash
Generate HMAC
Directly affect the user experience on devices.
Copy to Clipboard
Haptic Feedback
Invoke Function on Fragment
Invoke Function on Persistent Connection
Navigate
Subscribe to Notifications
Unsubscribe from Notifications
Trigger Event
Control how/when actions and workflows execute.
Delay
Repeat Execute Workflow
Communicate back and forth between web views and their parent context.
Send Message from Parent to Web View
Send Message from Web View to Parent
Contexts
Workflows can run where they’re needed.
→
Client-side: inside apps, directly affecting the user experience.
→
Server-side: inside the EMS, for secure operations and integrations.
Workflows can call other workflows, allowing a process to start client-side, continue on the server, and return again if needed.